
The Fourth Industrial Revolution: How 3D Printing and AI are Changing Manufacturing Forever
Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a significant role in the fourth industrial revolution by enabling automation, advanced robotics, and smart machines that can learn and make decisions.
Table of Contents
What do young upstarts like Tesla, Inc (founded in 2003 in San Carlos, California) and Relativity Space (founded in 2015 in Long Beach, California) have in common with multinational conglomerates founded in the 1800s?
Despite their differences in age and size, traditional companies like General Electric (founded in 1892 in Schenectady, New York) and Siemans (founded in 1847 in Berlin, Kingdom of Prussia) share surprising similarities with young upstart manufacturers like Tesla.
All of these companies are at the center of the fourth industrial revolution.

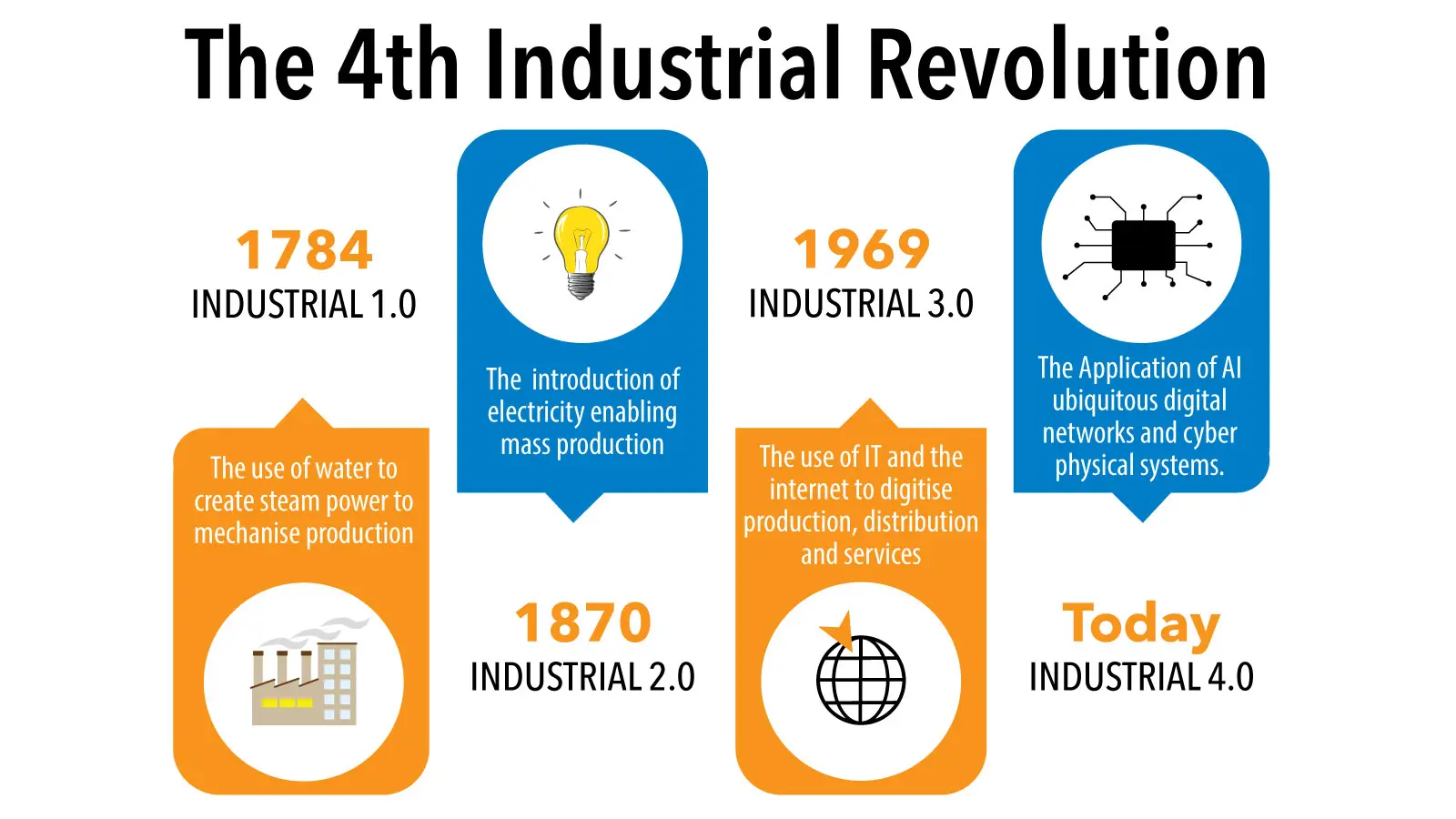
What is the Forth Industrial Revolution?
The fourth industrial revolution is a term used to describe the current trends in manufacturing, which build upon the previous three industrial revolutions:
- The first industrial revolution, which took place in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, was characterized by the mechanization of production through steam power.
- The second industrial revolution, which took place in the late 19th and early 20th centuries and was characterized by the introduction of electricity and mass production.
- The third industrial revolution, which took place in the late 20th century, was characterized by the digitalization of production through computers and automation.
The fourth industrial revolution is characterized by the fusion of technologies that blur the lines between the physical, digital, and biological worlds. This includes Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, 3D printing, and biochemical engineering.
Additive Manufacturing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has emerged as a key technology, revolutionizing how we design, produce and deliver products.
Using 3D printers, manufacturers can create complex geometries and intricate designs that were previously impossible with traditional manufacturing techniques. This offers new customization and flexibility, allowing companies to quickly and easily produce small batches of highly customized products.
3D printing processes are highly efficient, reducing waste and minimizing the need for expensive tooling and setup costs. This makes it ideal for producing parts on demand, reducing lead times, and enabling just-in-time manufacturing.
Subscribe to PrintNanny Newsletter
Interested in the latest innovations in Artificial Intelligence and Smart Manufacturing?
PrintNanny Newsletter
Subscribe to get informative posts like this one delivered to your email inbox.
Just-in-Time Manufacturing
Just-in-time manufacturing reduces waste by minimizing excess inventory and optimizing production processes. Compared to techniques of yesteryear, just-in-time manufacturers can respond quickly to changes in demand and easily customize products.
Digital Warehouses
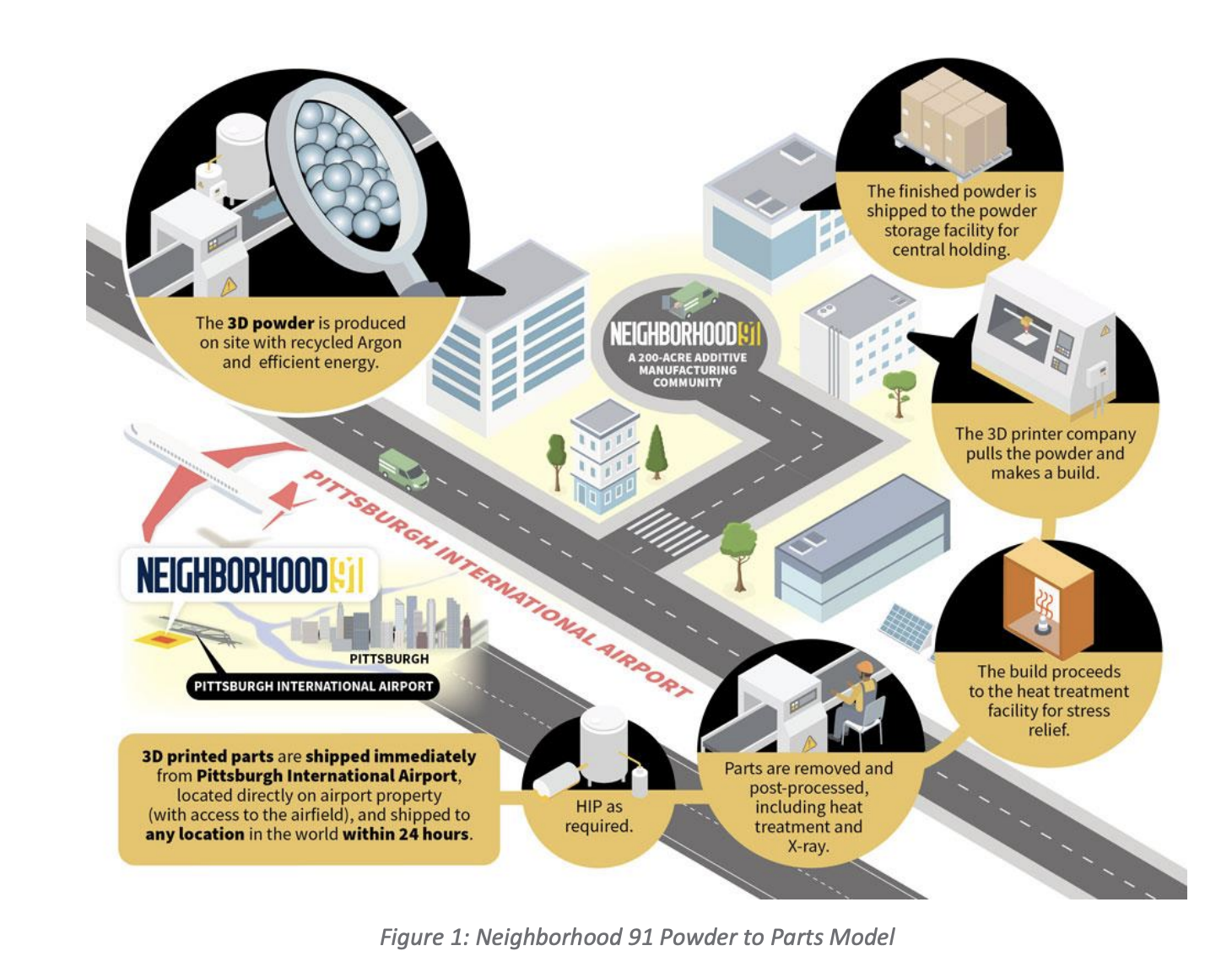
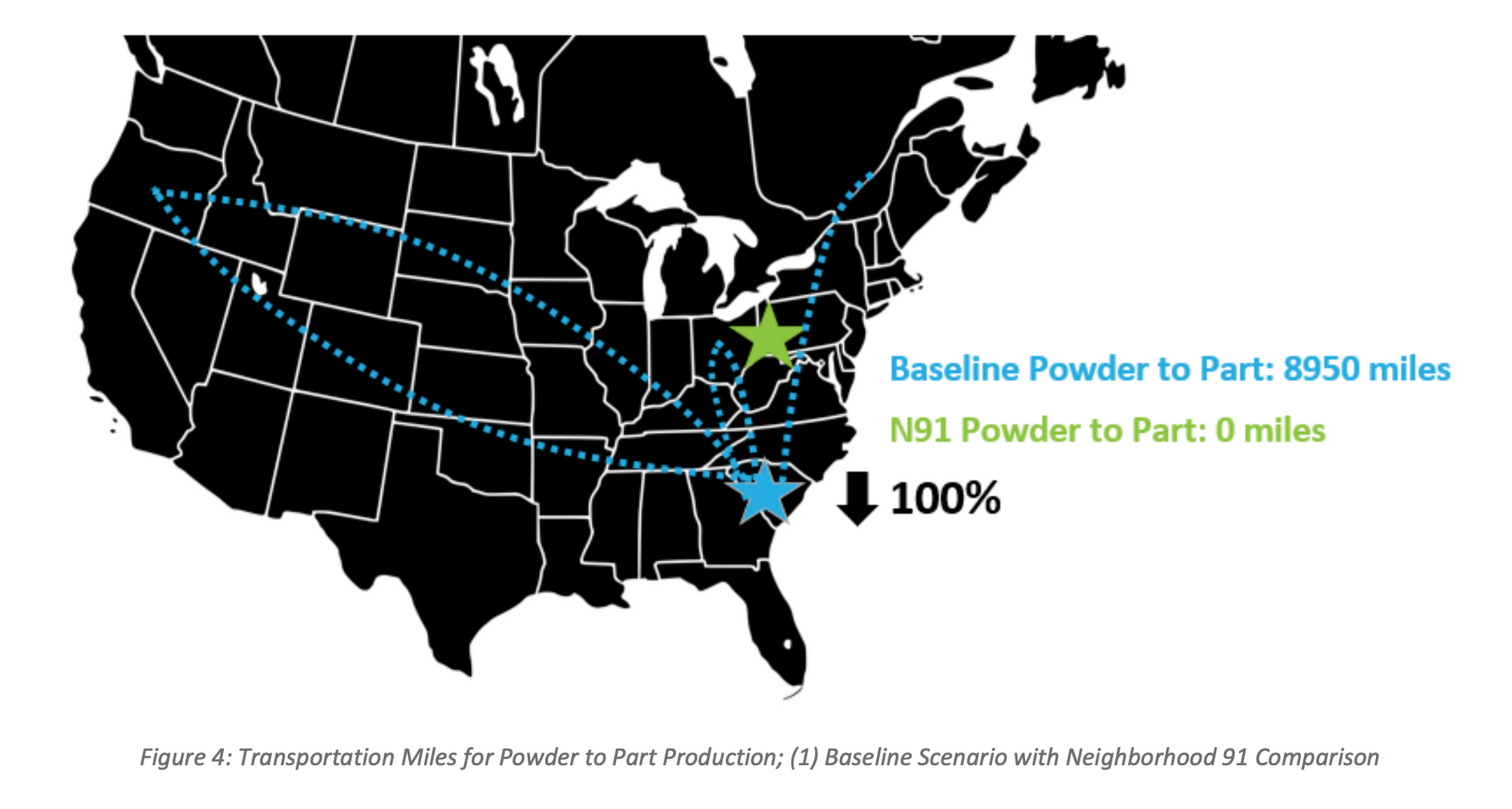
Companies like Xometry provide an on-demand manufacturing platform that leverages 3D printing technology to produce parts. On-demand manufacturing depends on digital warehousing, which enables customers to store their 3D printing designs and access them as needed.
Instead of shipping and storing pallets of finished physical products, companies now have the option to produce parts on-demand at a location close to the parts' destination.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a significant role in the fourth industrial revolution by enabling automation, advanced robotics, and smart machines that can learn and make decisions.
One of the key benefits of AI is the ability to automate routine tasks and processes, freeing human workers to focus on higher-value tasks that require creativity, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence.
Assembly Lines
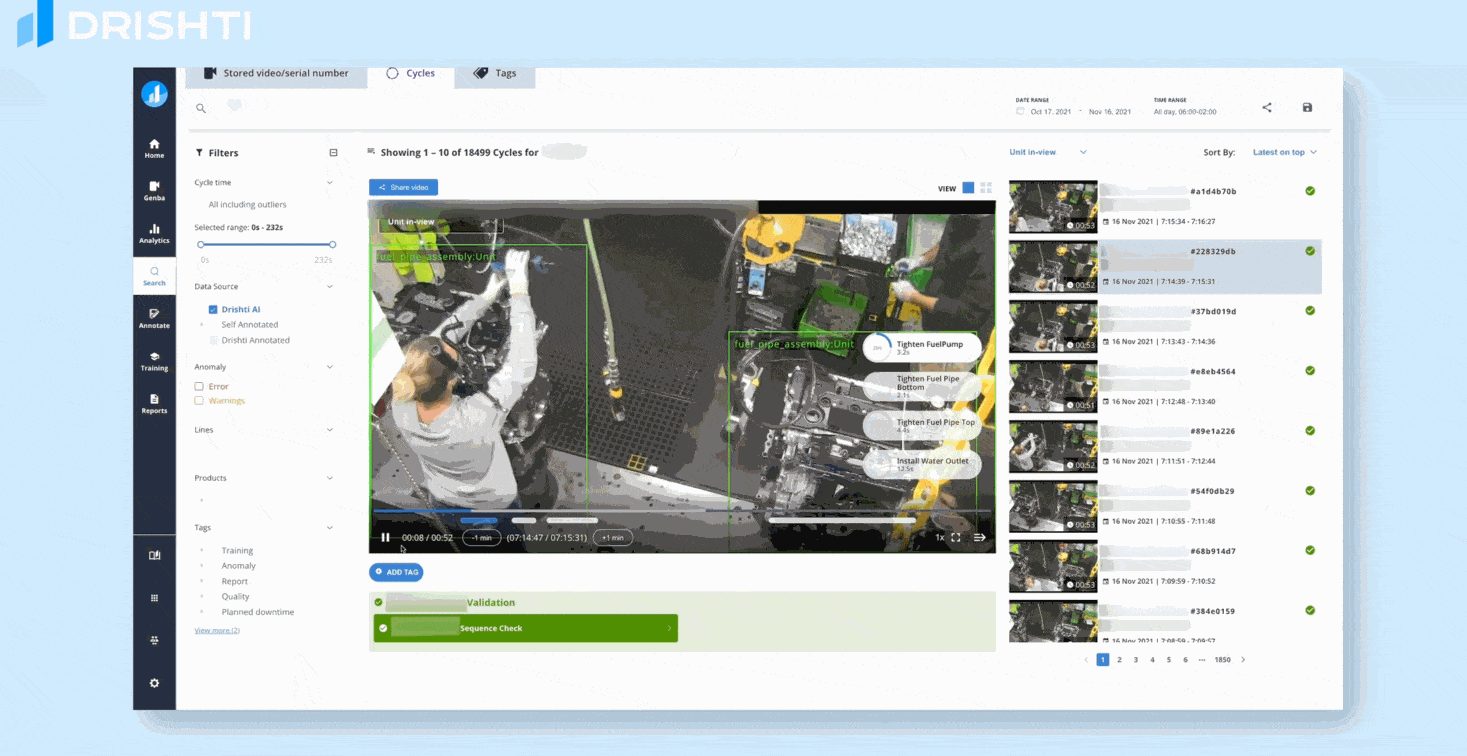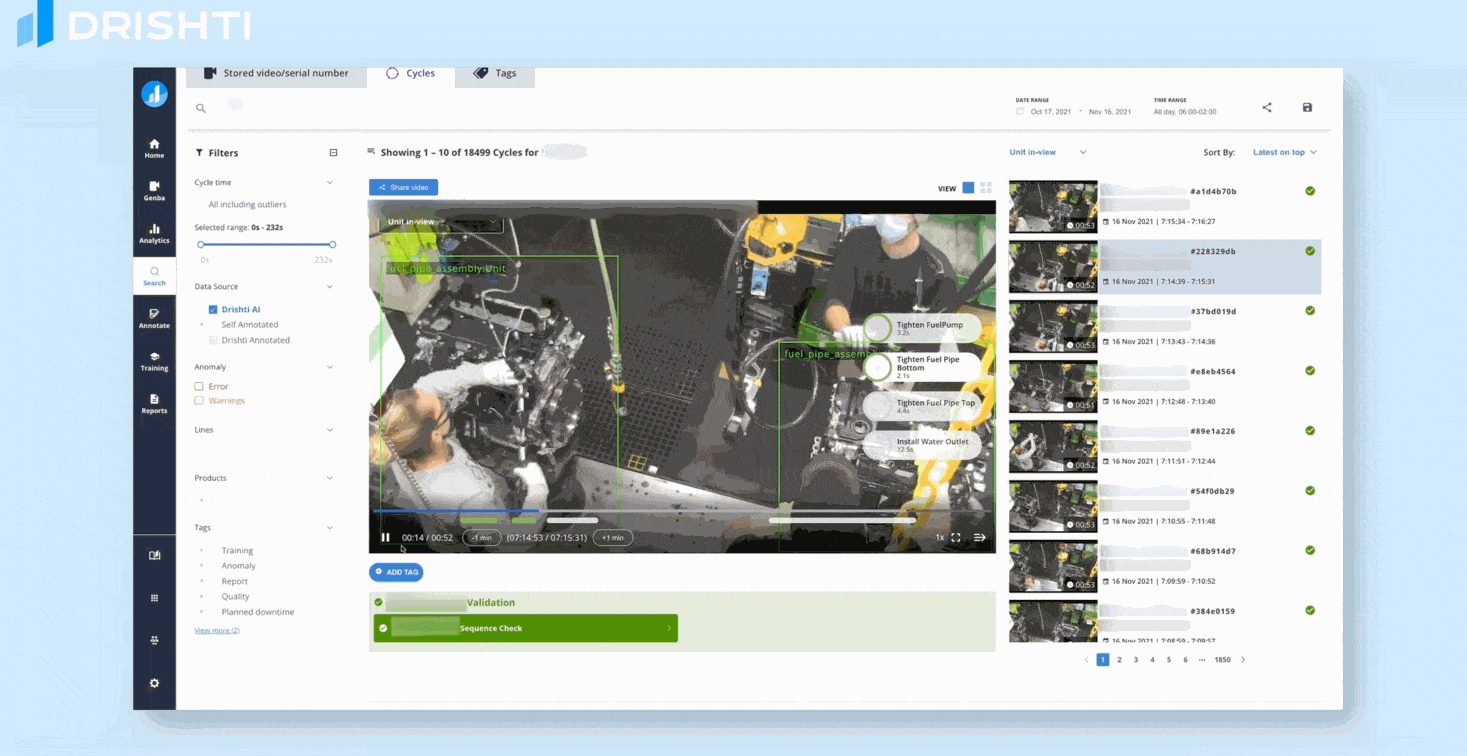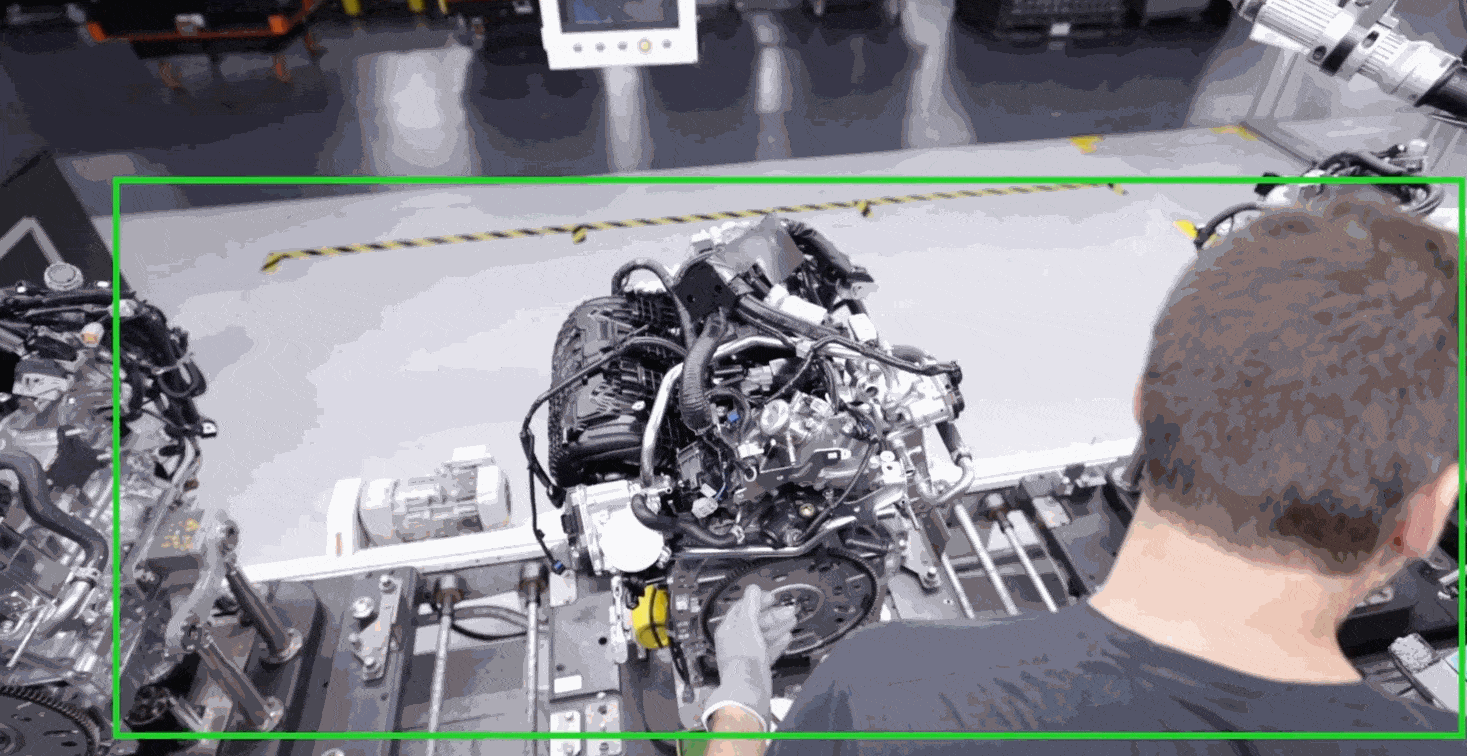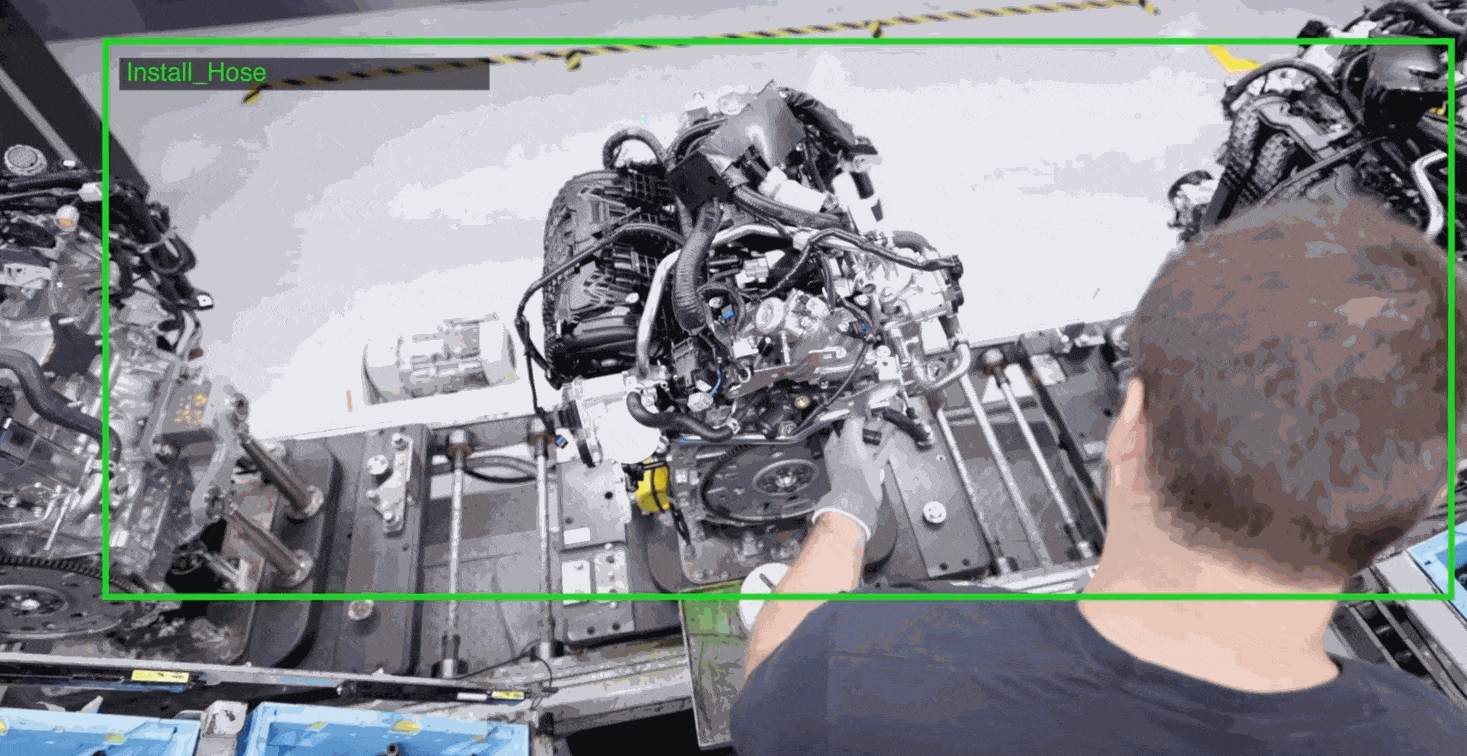
Computer vision is a powerful tool for manual assembly line quality control, enabling real-time identification and analysis of defects to improve product consistency and reduce errors. By automating visual inspection tasks, computer vision can increase efficiency and accuracy while reducing costs and improving overall quality.
Defective Parts
Products like PrintNanny.ai use computer vision to provide real-time monitoring and quality control during 3D printing process.
Generative Part Design
Generative AI is a category of artificial intelligence algorithms that generate new outputs. Examples include Stable Diffusion (text-to-image generator) by Stability.ai, and ChatGPT by OpenAI.
The designs generated by AI take into account desired weight, material, size, strength, and manfacturing methods. The final designs are often significantly lighter and stronger than designs produced by humans.
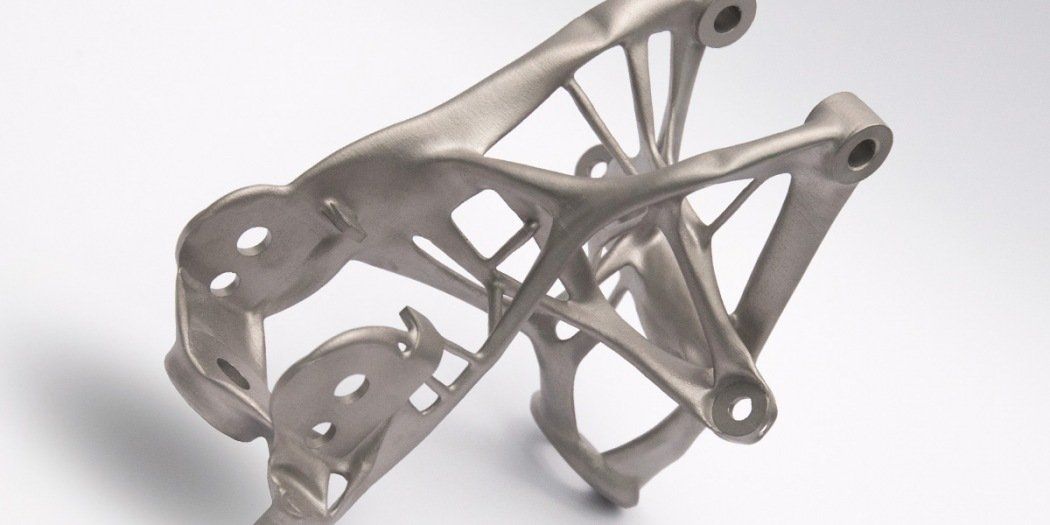
General Motors (GM) reported thousands of lbs of reduced mass across their vehicle after using AutoDesk's generative tool to design new parts, such as the seat bracket shown below.

PrintNanny.ai Newsletter
Join the newsletter to receive the latest updates in your inbox.




